US heart surgeon treats children lacking care in Libya's war
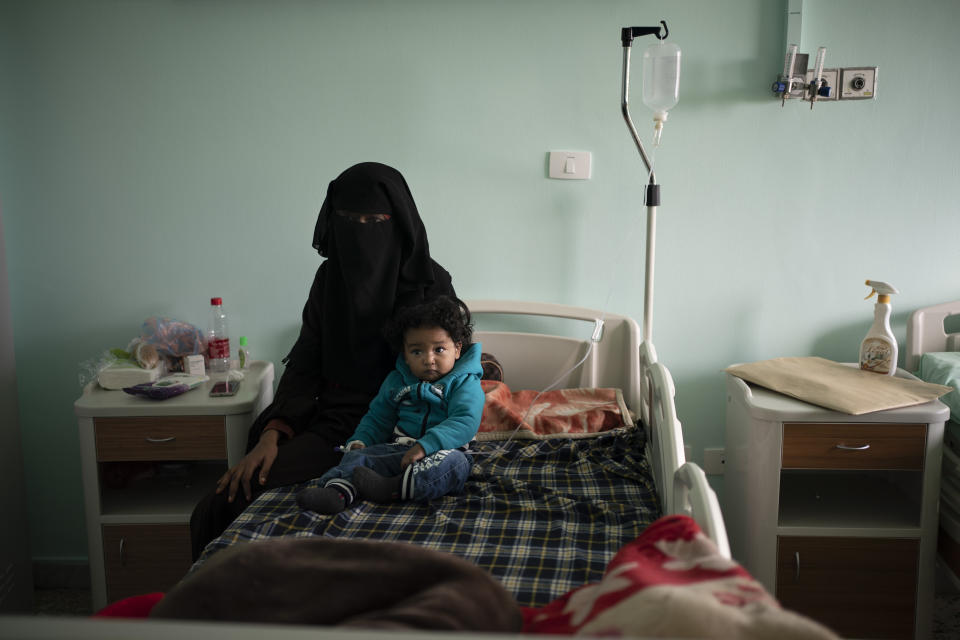
TRIPOLI, Libya (AP) — Yazan, a 1-year-old Libyan boy, was born with congenital heart disease. With just one chamber, the organ pumped so little blood that when Yazan cried, his skin turned black. Without surgery, he would not survive.
But Yazan's country, Libya, has only one heart surgeon who can't possibly perform surgeries on 1,200 or so infants born every year with heart defects. Of those, typically some 150 are in dire need of surgery and die in their first year, said William Novick, an American pediatric cardiac surgeon.
His international team of experts, part of the Novick Cardiac Alliance, regularly flies into Libya to perform surgery on patients like Yazan.
“To me this is simply an unacceptable situation that needs our attention,” said Novick, who lives in Memphis, Tennessee.
The medical trips help prop up Libya’s fragile health care system, which the World Health Organization has described as overburdened, inefficient and short of medicine and equipment.
Libya has been plunged into chaos since 2011, when a civil war toppled longtime dictator Moammar Gadhafi, who was later killed. Eastern-based opposition forces attacked Tripoli last spring to wrest it from control of the weak U.N.-backed government. The fierce round of fighting has killed hundreds of civilians, including at least 13 children since mid-January.
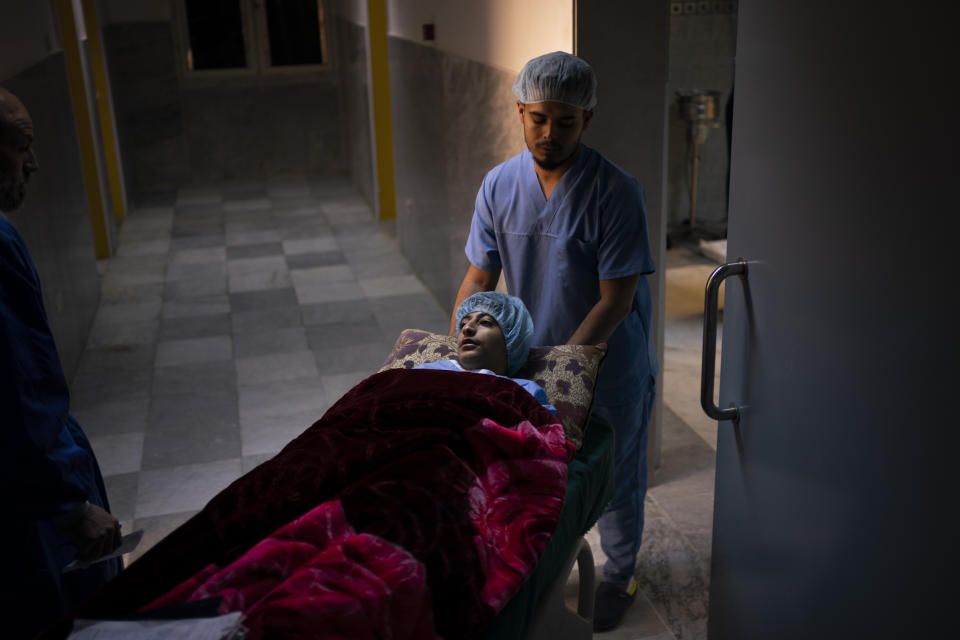
Novick's team was the best, and perhaps last, hope for Yazan. But that meant his family had to travel to the most dangerous place in the war-ravaged country — the capital Tripoli, where the Tajoura National Heart Center is located.
Yazan’s odyssey from his small desert hometown barely skirted the war’s front lines. With key highways blocked because of fighting, his family took a 1,500-kilometer (932-mile) detour.
“You can’t come to Tripoli like before,” said Yazan's father, Im Saleh Mohamed Abudulfetah.
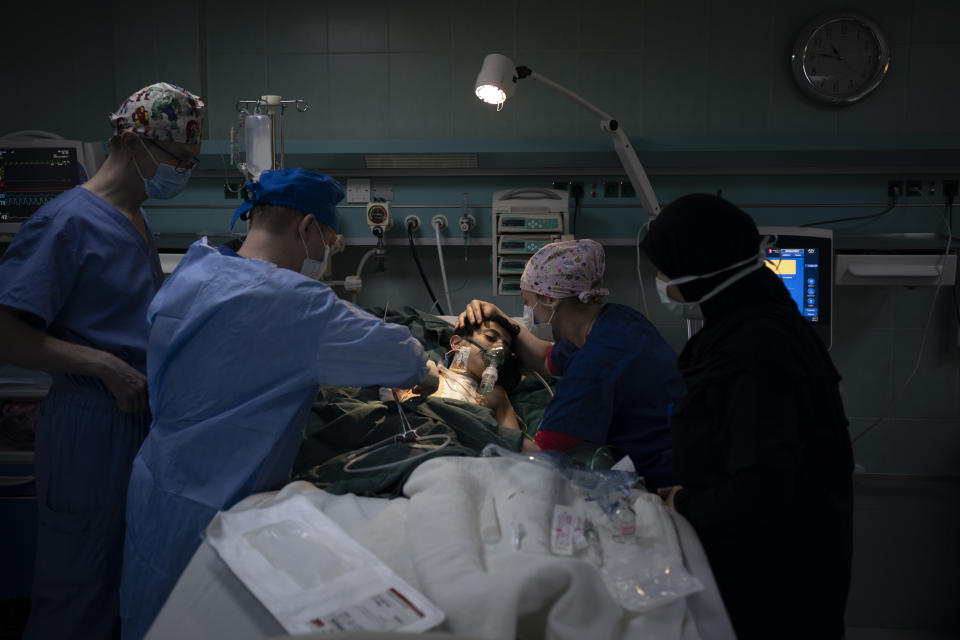
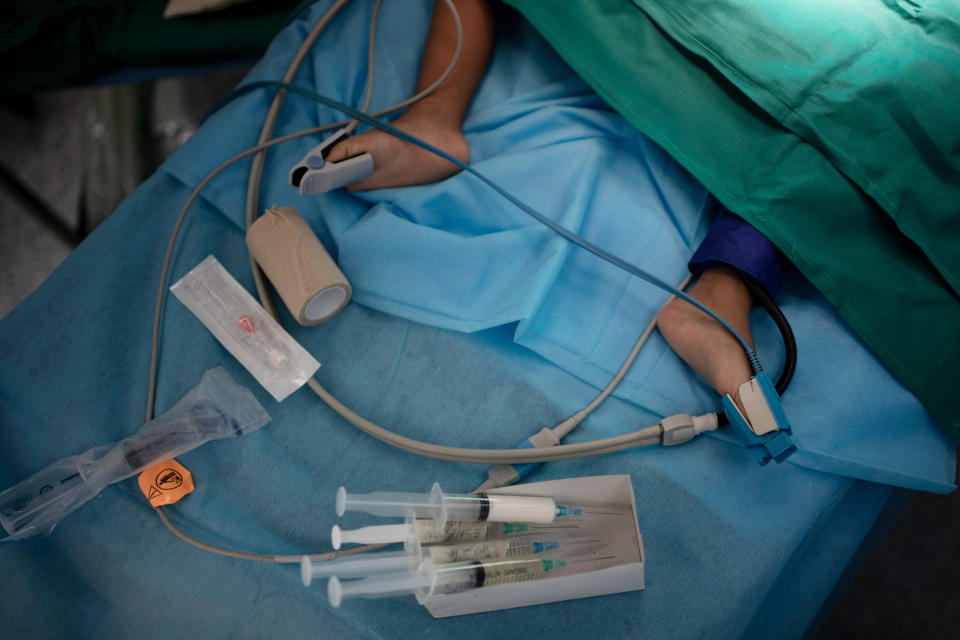
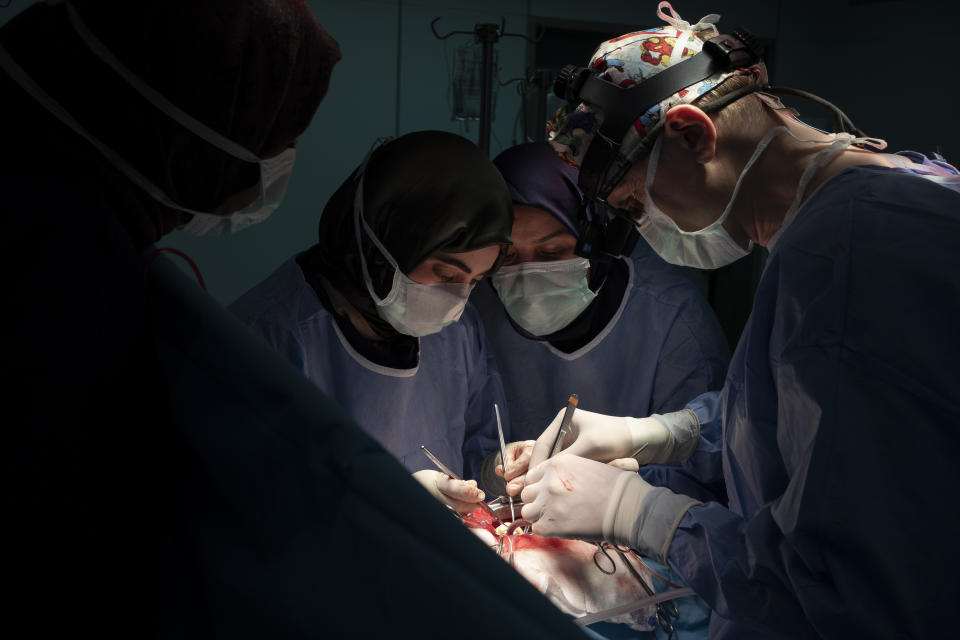
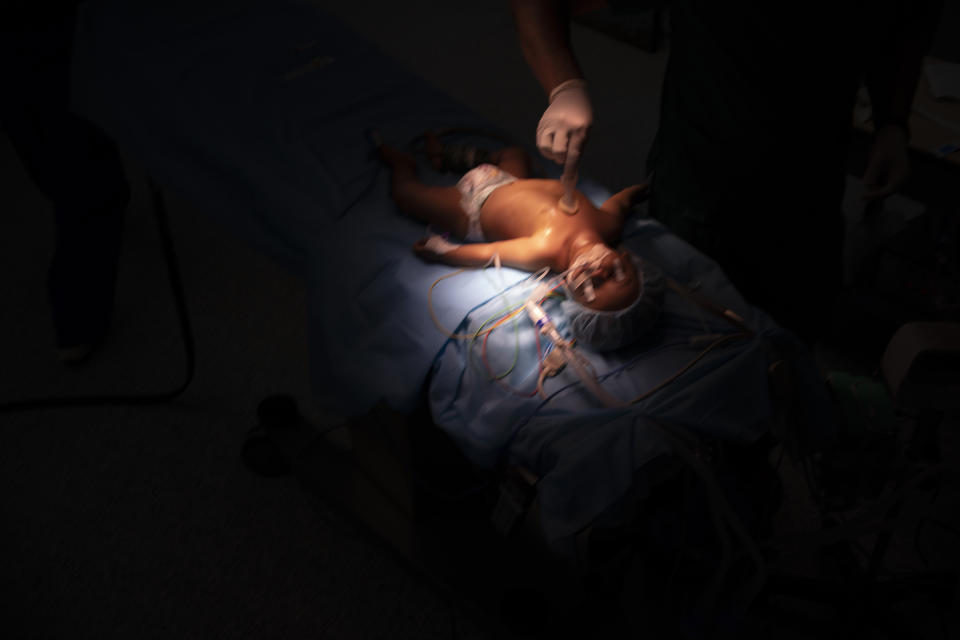
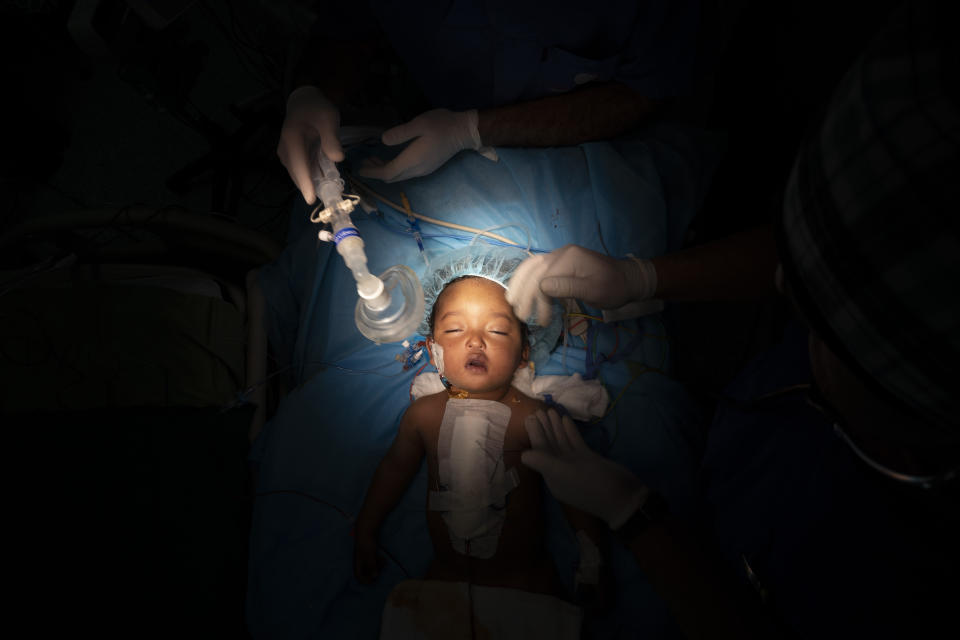
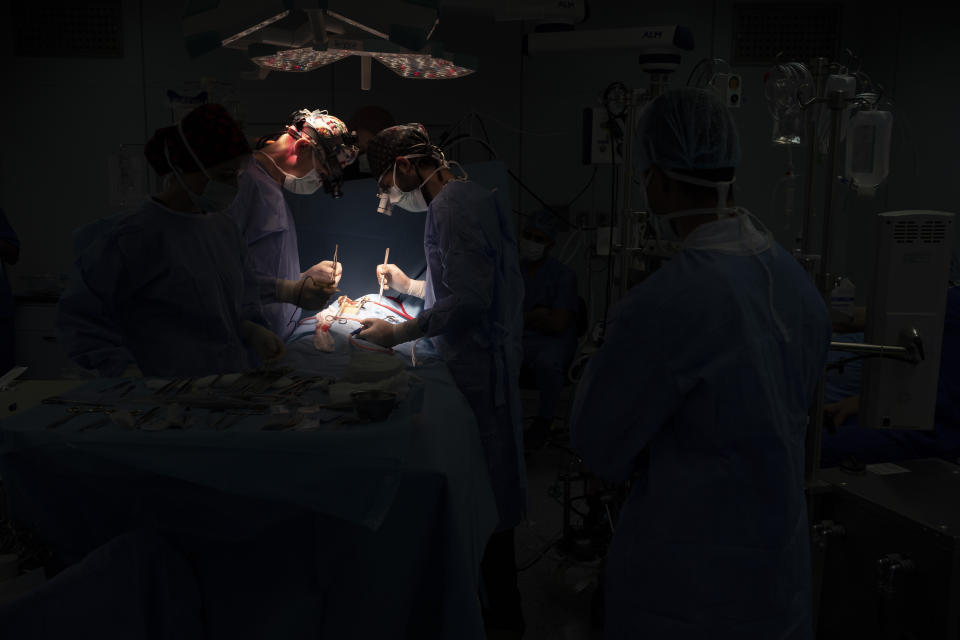
On Feb. 26, Yazan’s perilous trek culminated in a five-hour surgery. Yazan is one of 1,000 children treated by Novick’s group since it first came to Libya after the 2011 uprising.
In the operating room, Novick and his team chatted calmly as they cut open Yazan’s chest. They sewed together two large veins carrying blood from Yazan’s head and connected them to his pulmonary artery. That sent oxygenated blood straight to his lungs.
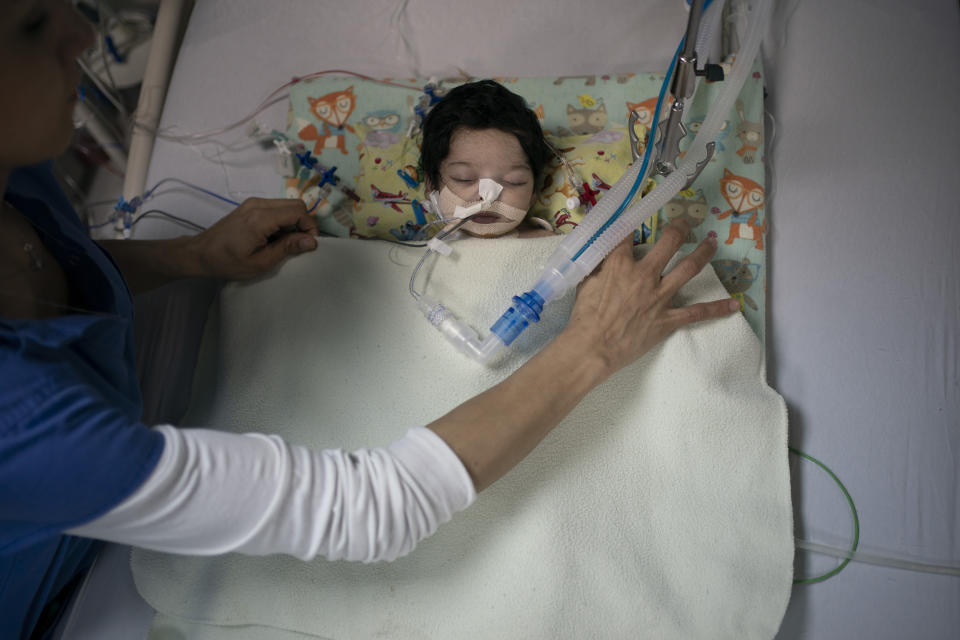
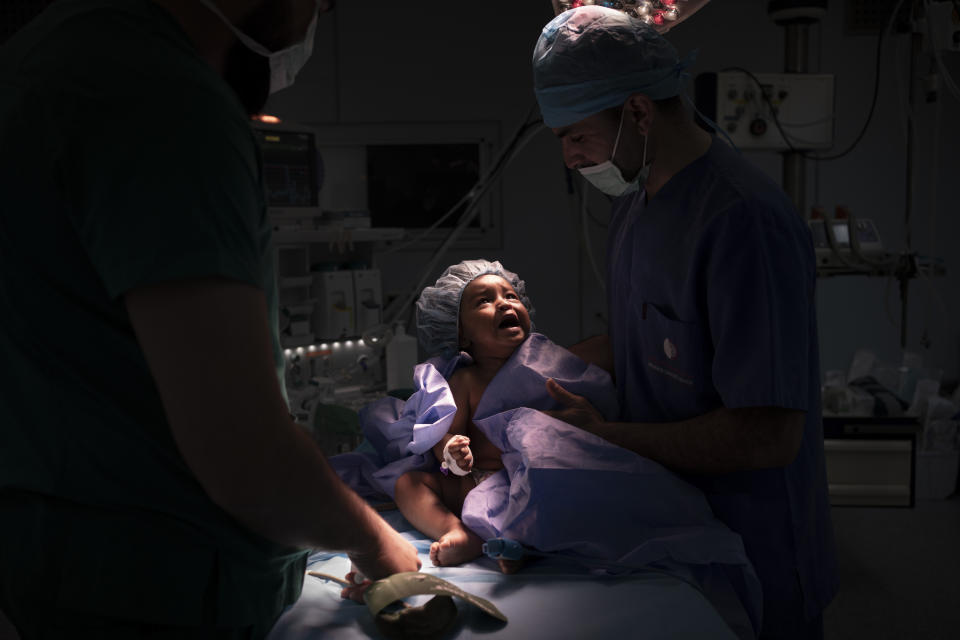
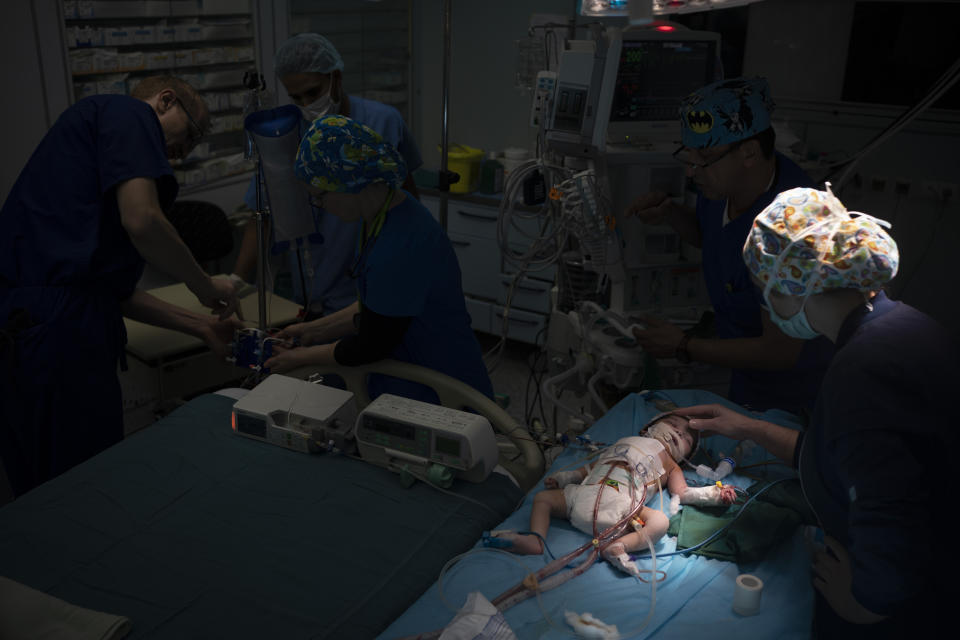
Eventually, exhausted nurses wheeled Yazan out of the operating theater, his tiny body covered in bandages and tubes, to tell his parents the news. They expected Yazan to recover well, and with a follow-up operation, live a normal life.
Under the fluorescent light of the intensive care unit, Abudulfetah touched his baby’s soft hair, murmuring words of prayer. Yazan’s belly rose and fell with steady breath. His cheeks were even flushed a subtle pink.
As a young medical resident at the University of Alabama, Novick, now 66, witnessed the suffering of children with congenital heart disease and the staggering disparities in health services. He became determined to try to give children with heart problems the care they need, no matter where they’re born.
While still a resident, Novick began recruiting experts to help him trek to places where treatable heart disease means death due to a shortage of specialists and other restrictions.
Over nearly three decades, Novick and his colleagues have made hundreds of trips to 32 countries including Ukraine, Nigeria, Iraq, Iran and Columbia.
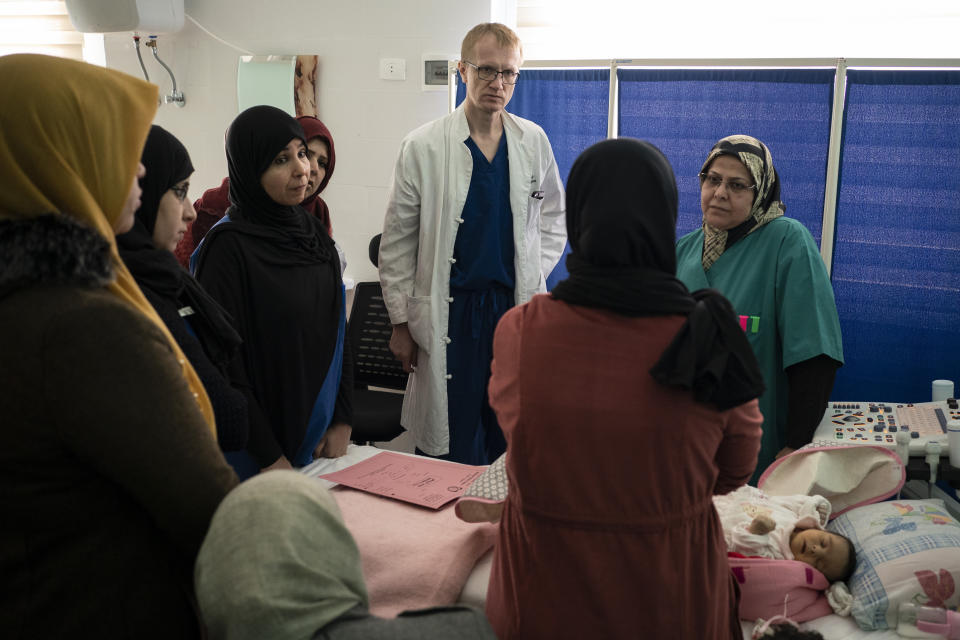
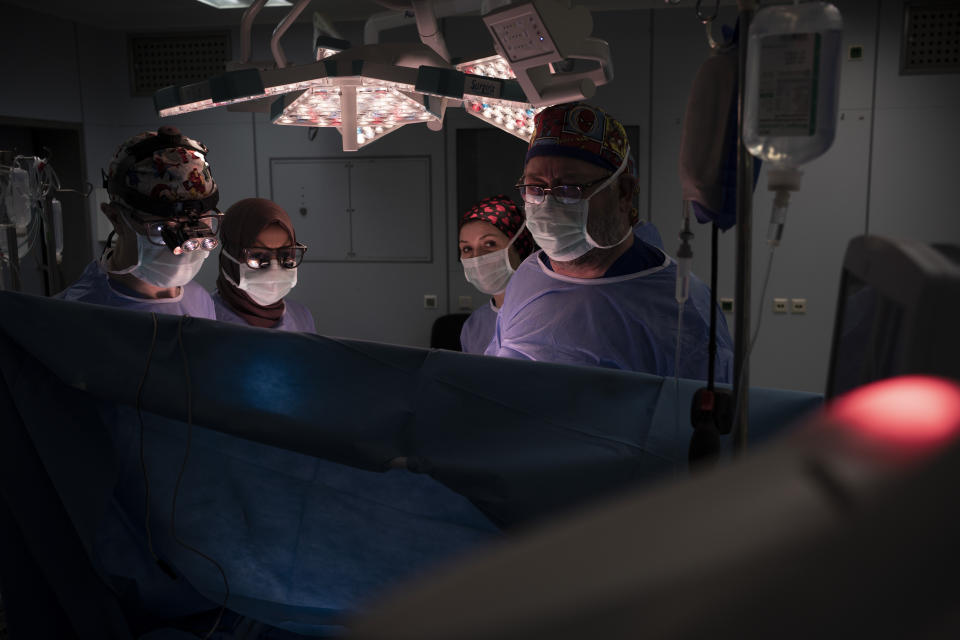
Novick’s Libya team in February consisted of 20 volunteers: cardiologists, surgeons, nurses and anesthesiologists. The Associated Press accompanied them as they performed 10 complex open-heart surgeries in the country’s west. The group flies home from Tripoli next week after completing dozens more operations.
Political power in Libya today is divided between the two rival governments in the east and west of the country and a patchwork of armed groups and foreign countries that support either administration.
“We’re on both sides of the conflict zone,” said Novick. “And that is a specific goal of ours, to be apolitical and help the children.”
Novick’s group not only drops in a few times a year, but also trains Libyan doctors and nurses to build up the country’s critical health care system.
“We’re not going to be here forever and we shouldn’t be here forever,” he said.