Astronauts unfurl final roll-out solar array (for now) at space station in record-tying spacewalk
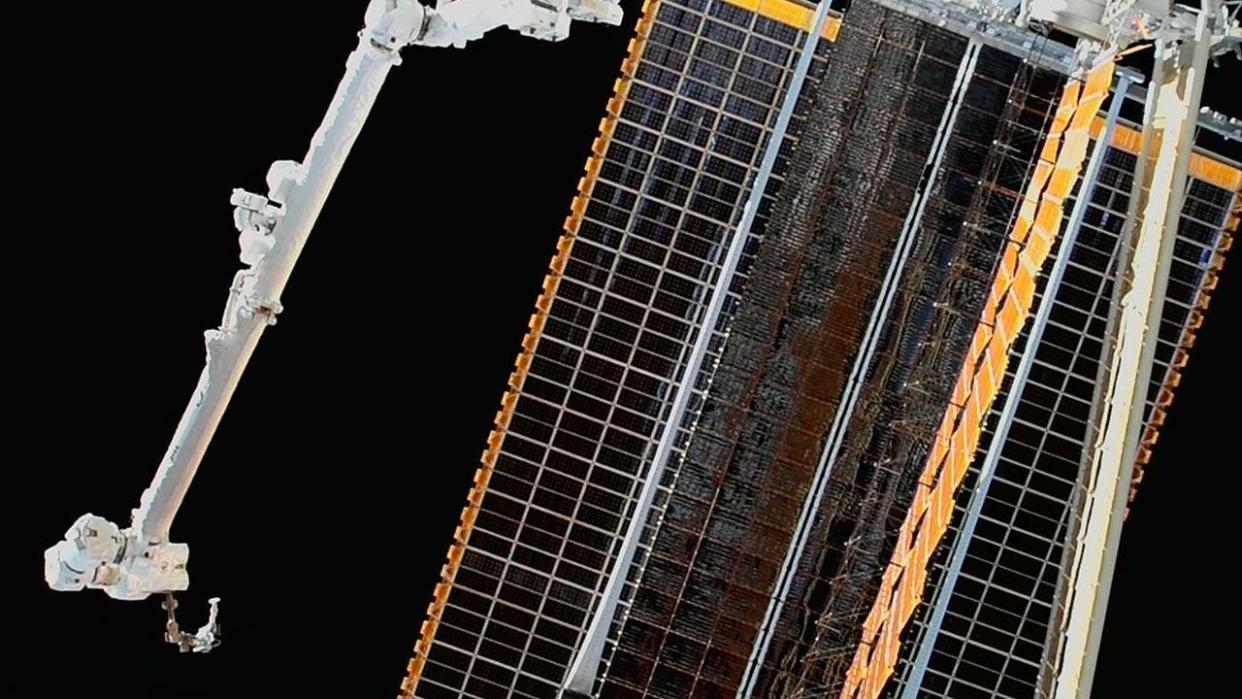

Two NASA astronauts deployed the sixth and last (for now) upgraded solar array outside of the International Space Station, increasing the orbital laboratory's power supply while tying an American spacewalk record.
Warren "Woody" Hoburg and Stephen Bowen completed their second extravehicular activity (EVA) together on Thursday (June 15), just under a week after they successfully installed the fifth International Space Station (ISS) Roll-Out Solar Array (iROSA) on June 9, augmenting the complex's 1A power channel. On Thursday's spacewalk, the two Expedition 69 crewmates repeated almost the same steps, only this time they were focused on the 1B power channel located on the opposite side of the station's starboard truss.
The spacewalk began at 8:42 a.m. EDT (1242 GMT), when both astronauts switched their suits to internal battery power. After emerging from the U.S. Quest airlock, Hoburg and Bowen went to work preparing the array for its removal from a temporary storage platform and, in Hoburg's case, boarding the end of the station's Canadarm2 robotic arm from where he would carry the iROSA to its installation point.
Emirati astronaut Sultan AlNeyadi controlled the arm from inside the station, moving Hoburg and the 720-pound (330 kilograms) array to the S4 truss. Meanwhile, Bowen made his way to the same area.
Related: The most memorable spacewalks of all time in pictures
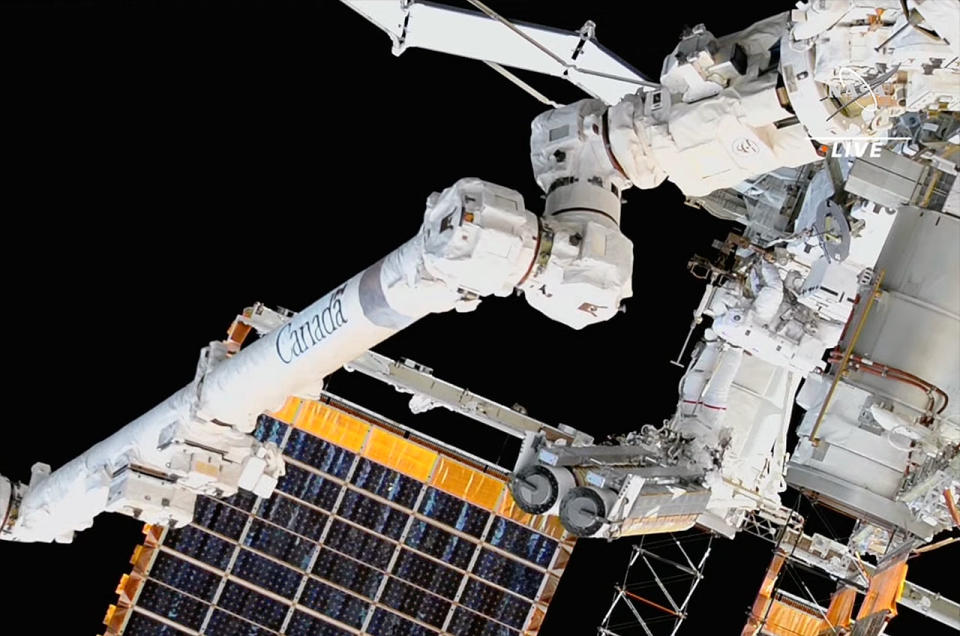

The duo then took turns holding onto the iROSA as they aligned it with its mounting bracket, a triangular attach point that was assembled and installed on a previous spacewalk. Hoburg and Bowen then drove bolts to secure the array to the station before releasing the hinges that held the iROSA in its folded launch configuration.
The spacewalkers then took a break from working on the array's installation to get ahead on cleaning up their worksites as they waited for the space station to move into Earth's shadow. The hold was to ensure the legacy IB solar array was not generating power when work began to tie the new iROSA into the power channel.
Once the station was in eclipse, Hoburg and Bowen set to work connecting cables to the new array assembly. They were then ready to deploy the wing.
Each iROSA is 60 feet long by 20 feet wide (18.2 meters by 6 meters). When unfurled, each overlays its corresponding legacy solar array by a little more than a half. As each produces more than 20 kilowatts of electricity, with six new arrays installed, the station is now capable of a 30% increase in power production over the station's legacy arrays alone.
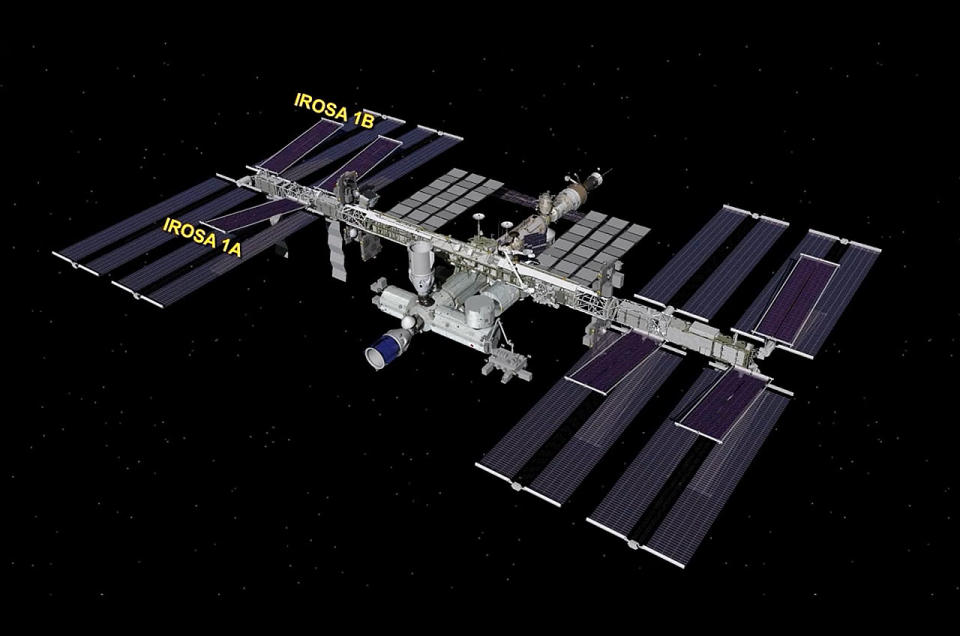
It has taken two years — less one day — to deploy all six iROSA assemblies, with the first unfurled on June 16, 2021. NASA and Boeing have a plan for a fourth set of roll-out arrays to further augment the International Space Station's power supply. These arrays, which would be the seventh and eighth to be installed, are targeted for delivery to the orbiting laboratory in the 2025 timeframe.
Once out of Earth's shadow, Hoburg released two bolts allowing the iROSA to unfurl. The potential energy stored by the rolled-up carbon composite booms caused the array to unroll on its own to its full length, with no motor needed.
During the rollout, a triangular panel on the array appeared to have become snagged such that it didn't lie flat. Hoburg photographed the issue for further study, but it is not expected to affect the performance of the array. After about 12 minutes, when the array was fully deployed, Hoburg tightened two final bolts to tension it.
With the sixth iROSA installed and unfurled, Hoburg and Bowen worked on their remaining cleanup tasks, returning items to the airlock or where they are stowed on the station's exterior. They then each were assigned get-ahead tasks, including retrieving a connector tool from a tool box and repositioning a foot restraint.

RELATED STORIES:
— Spacewalks: How they work and major milestones
— The most memorable spacewalks in history
— The International Space Station: Facts, history and tracking
After 5 hours and 35 minutes, the spacewalk came to an end at 2:17 p.m. EDT (1817 GMT) as re-pressurization of the Quest airlock began.
Thursday's EVA was the second for Hoburg, who now has spent a total of 11 hours and 38 minutes in the vacuum of space.
This was the 10th spacewalk for Bowen, who now ties former NASA astronauts Michael Lopez-Alegria, Bob Behnken, Peggy Whitson and Chris Cassidy for the most EVAs conducted by an American. With a total of 65 hours and 57 minutes, Bowen now ranks third in the world for time spent on spacewalks. He is surpassed only by Lopez-Alegria, who has logged 67 hours and 40 minutes, and Russian cosmonaut Anatoly Solovyev, who has spent 78 hours and 28 minutes on EVA.
Thursday's spacewalk was the eighth this year and the 265th dedicated to the assembly and maintenance of the International Space Station since 1998.
