Post-COVID heart damage alarms researchers: 'There was a black hole' in infected cells
Shelby Hedgecock contracted the coronavirus in April and thought she had fought through the worst of it — the intense headaches, severe gastrointestinal distress and debilitating fatigue — but early last month she started experiencing chest pain and a pounding heartbeat. Her doctor put her on a cardiac monitor and ordered blood tests, which indicated that the previously healthy 29-year-old had sustained heart damage, likely from her bout with COVID-19.
“I never thought I would have to worry about a heart attack at 29 years old,” Hedgecock told Yahoo News in an interview. “I didn’t have any complications before COVID-19 — no preexisting conditions, no heart issues. I can deal with my taste and smell being dull, I can fight through the debilitating fatigue, but your heart has to last you a really long time.”
Hedgecock’s primary-care physician has referred her to a cardiologist she will see this week; the heart monitor revealed that Hedgecock’s pulse rate is wildly irregular, ranging from 49 to 189 beats per minute, and she has elevated inflammatory markers and platelet counts. She was told to go to the emergency room if her chest pain intensifies before she can see the specialist. A former personal trainer who is now out of breath just from walking around the room, Hedgecock is worried about what the future holds.
She is far from alone in her struggle. Dr. Ossama Samuel is a cardiologist at New York’s Mount Sinai Hospital, where he routinely sees coronavirus survivors who are contending with cardiac complications. Samuel said his team has treated three young and otherwise healthy coronavirus patients who have developed myocarditis — an inflammation of the heart muscle — weeks to months after recovering from the virus.
Myocarditis can affect how the heart pumps blood and trigger rapid or abnormal heart rhythms. It is particularly dangerous for athletes, doctors say, because it can go undetected and can result in a heart attack during strenuous exercise. In recent weeks, some collegiate athletes have reported cardiac complications from the coronavirus, underscoring the seriousness of the condition.
Last month, former Florida State basketball center Michael Ojo died from a heart attack in Serbia; Ojo had recovered from the coronavirus before he collapsed on the basketball court. An Ohio State University cardiologist found that between 10 and 13 percent of university athletes who had recovered from COVID-19 had myocarditis. When the Big Ten athletic conference announced the cancellation of its season last month, Commissioner Kevin Warren cited the risk of heart failure in athletes. Researchers have estimated that up to 20 percent of people who get the coronavirus sustain heart damage.
Samuel said he feels an obligation to warn people, particularly since some of the patients he and Mount Sinai colleagues have seen with myocarditis had only mild cases of the coronavirus months ago.
“We are now seeing people three months after COVID who have pericarditis [inflammation of the sac around the heart] or myocarditis,” Samuel said. He said he believes a small fraction of coronavirus survivors are sustaining heart damage, “but when a disease is so widespread it is concerning that a tiny fraction is still sizable.”
Samuel said he worries particularly about athletes participating in team sports, since many live together and spend time in close quarters. Teammates may all get the coronavirus and recover together, Samuel said, but “the one who really gets that crazy myocarditis could be at risk of dying through exercise or training.”
“It’s a concern about what do you do: Should we do sports in general, should we do it in schools, should we do it in college, should we just do it for professionals who understand the risk and they're getting paid?” Samuel asked. “I hope we don’t scare the public, but we should make people aware.”
Samuel is recommending that patients recovering from COVID-19 with myocarditis avoid workouts for three to six months.
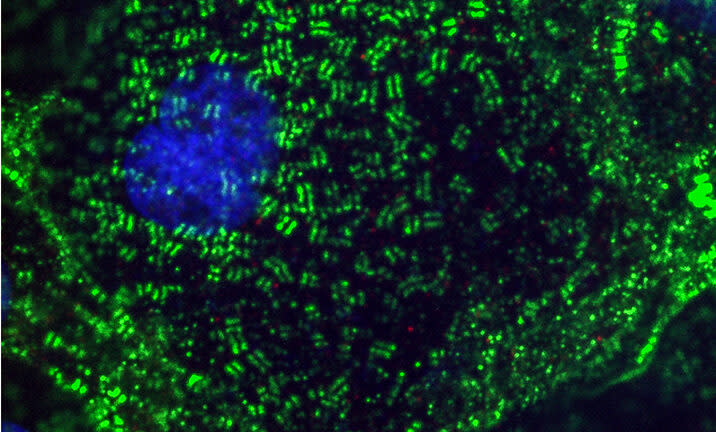
Todd McDevitt, who runs a stem-cell lab at Gladstone Institutes, which is affiliated with the University of California at San Francisco, recently published images that show how the coronavirus can directly invade the heart muscle. McDevitt said he was so alarmed when he saw a sample of heart muscle cells in a petri dish get “diced” by the coronavirus that he had trouble sleeping for nights afterward.

McDevitt said his team’s research was spurred by their desire to understand if the coronavirus is entering heart cells and how it is affecting them. He was surprised to see the heart muscle samples he was studying react to a very small amount of the coronavirus, usually within 24 to 48 hours. He said the virus decimated the heart cells in his petri dishes.
“Cell nuclei — the hubs of all the genetic information, all of the nuclear DNA — in many of the cells were gone,” McDevitt said. “There was a black hole literally where we would normally see the nuclear DNA. That’s also pretty bizarre.”
While McDevitt’s study has not yet been peer-reviewed — it is still in pre-print — he said he felt compelled to share the findings as soon as possible. He said his team also sampled tissues from three COVID-19 patient autopsies and found similar damage in the heart muscles of those patients, none of whom had been flagged for myocarditis or heart problems while they were alive.
“This is probably not the whole story yet, but we think we have insights into the beginning of when the virus would get into some of these people and what it might be doing that is concerning enough that we should probably let people know, because clinicians need to be thinking about this,” McDevitt said in an interview. “We don’t have any means of bringing heart muscle back. ... This virus is [causing] a very different type of injury, and one we haven't seen before.”
McDevitt said the chopped-up heart muscles he and his colleagues saw are so concerning because when the microfibers in the muscle are damaged, the heart can’t properly contract.
“If heart muscle cells are damaged and they can’t regenerate themselves, then what you’re looking at is someone who could prematurely have heart failure or heart disease due to the virus,” McDevitt said. “This could be a warning sign for a potential wave of heart disease that we could see in the future, and it’s in the survivors — that’s the concern.”
McDevitt said he believes the risk of heart disease is serious and one people should consider as they assess their own risk of getting the coronavirus.
“I am more scared today of contracting the virus, by far, than I was four months ago,” he said.
The medical journal the Lancet recently reported that an 11-year-old child had died of myocarditis and heart failure after a bout of COVID-induced multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C). An autopsy showed coronavirus embedded in the child’s cardiac tissue.
A recent study from Germany found that 78 percent of patients who had recovered from the coronavirus and who had only mild to moderate symptoms while ill with the disease had indications of cardiac involvement on MRIs conducted more than two months after their initial infection. Lead investigator Eike Nagel said it is concerning to see such widespread cardiac impact; six in 10 of the patients Nagel’s team studied experienced ongoing myocardial inflammation.
“We found an astonishingly high level of cardiac involvement approximately two months after COVID infection,” Nagel said in an email. “These changes are much milder than observed in patients with severe acute myocarditis.”
The scale of the cardiac impact on relatively healthy, young patients surprised many doctors. Nagel said the findings are significant “on a population basis,” and that the impact of COVID-19 on the heart must be studied more.

Dr. Gregg Fonarow, chief of UCLA’s Division of Cardiology and director of the Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, said the picture is evolving, but the new studies showing cardiac impact in even young people with mild cases of COVID-19 have raised troubling new questions.
“We really do need to take seriously individuals that have had the infection and are having continued symptoms, [and] not just dismiss those symptoms,” Fonarow said. “There could be, in those who had milder or even asymptomatic cases, the potential for cardiac risk.”
Fonarow said it is important to understand whether a “more proactive screening and treatment approach” is needed to better address the needs of patients who have recovered from the coronavirus and who may still have weakened heart function. Fonarow said he found McDevitt’s research to be potentially significant because it proves “from a mechanistic standpoint that there can be direct cardiac injury from the virus itself.”
“Even if it were going to impact, say, 2 percent of the people that had COVID-19, when you think of the millions that have been infected, that ends up in absolute terms being a very large number of individuals,” Fonarow said in an interview. “You don’t want people to be unduly alarmed, but on the other hand you don’t want individuals to be complacent about, ‘Oh, the mortality rate is so low with COVID-19, I don’t really care if I’m infected because the chances that it will immediately or in the next few weeks kill me is small enough, I don’t need to be concerned.’ There are other consequences.”
_____
Read more from Yahoo News:

